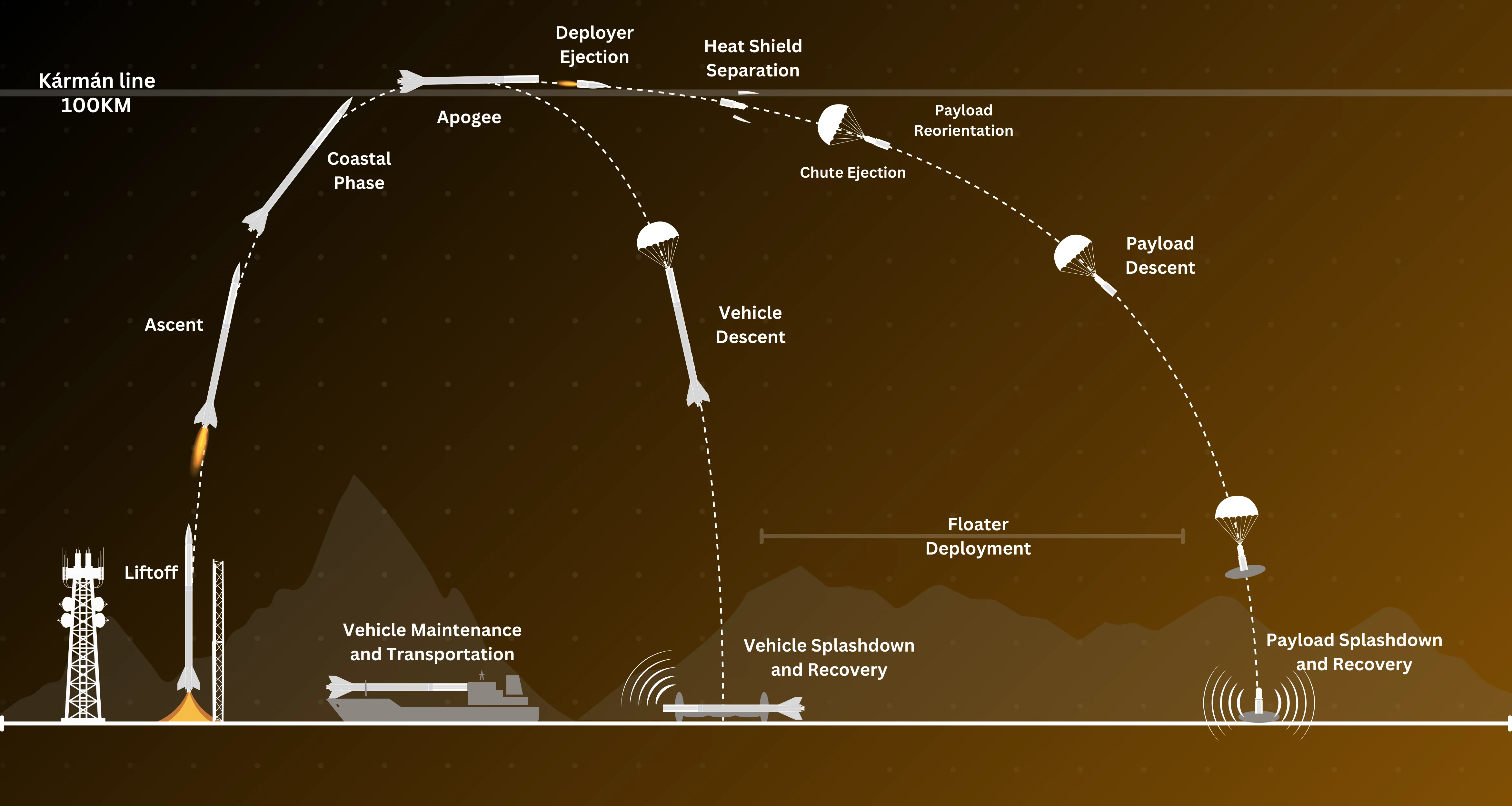
Explore Suborbit with BAAS

A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched. Hence, it will not complete one orbital revolution, will not become an artificial satellite nor will it reach escape velocity.
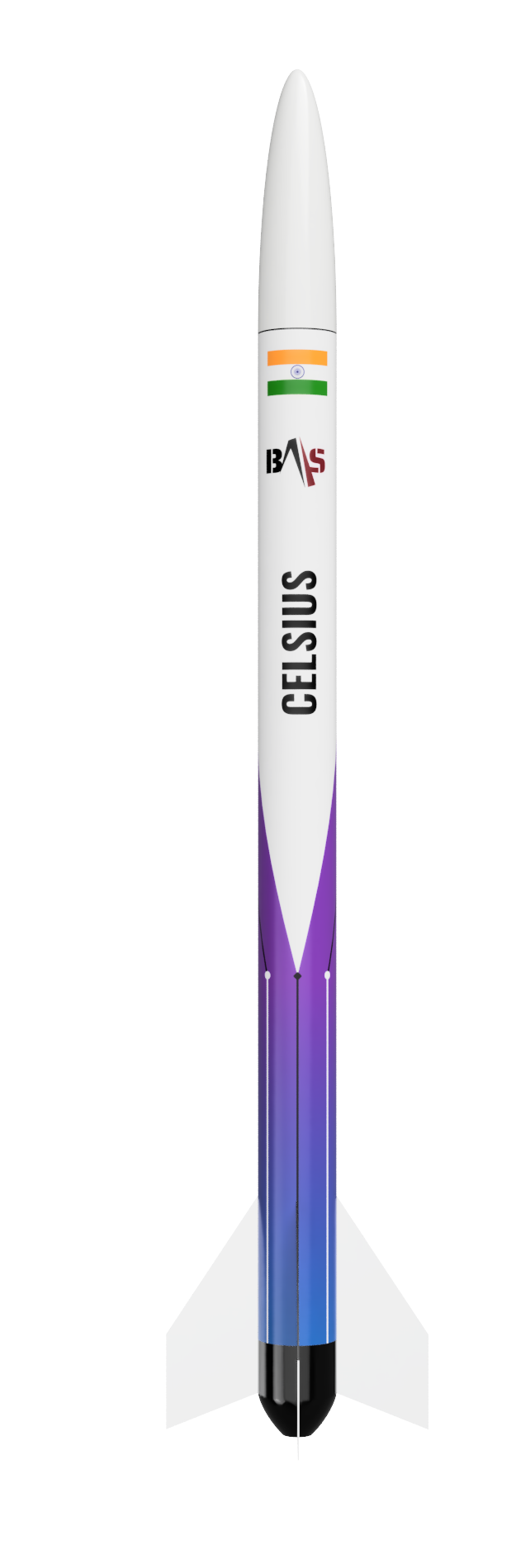
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km (30 to 90 miles) above the surface of the Earth.
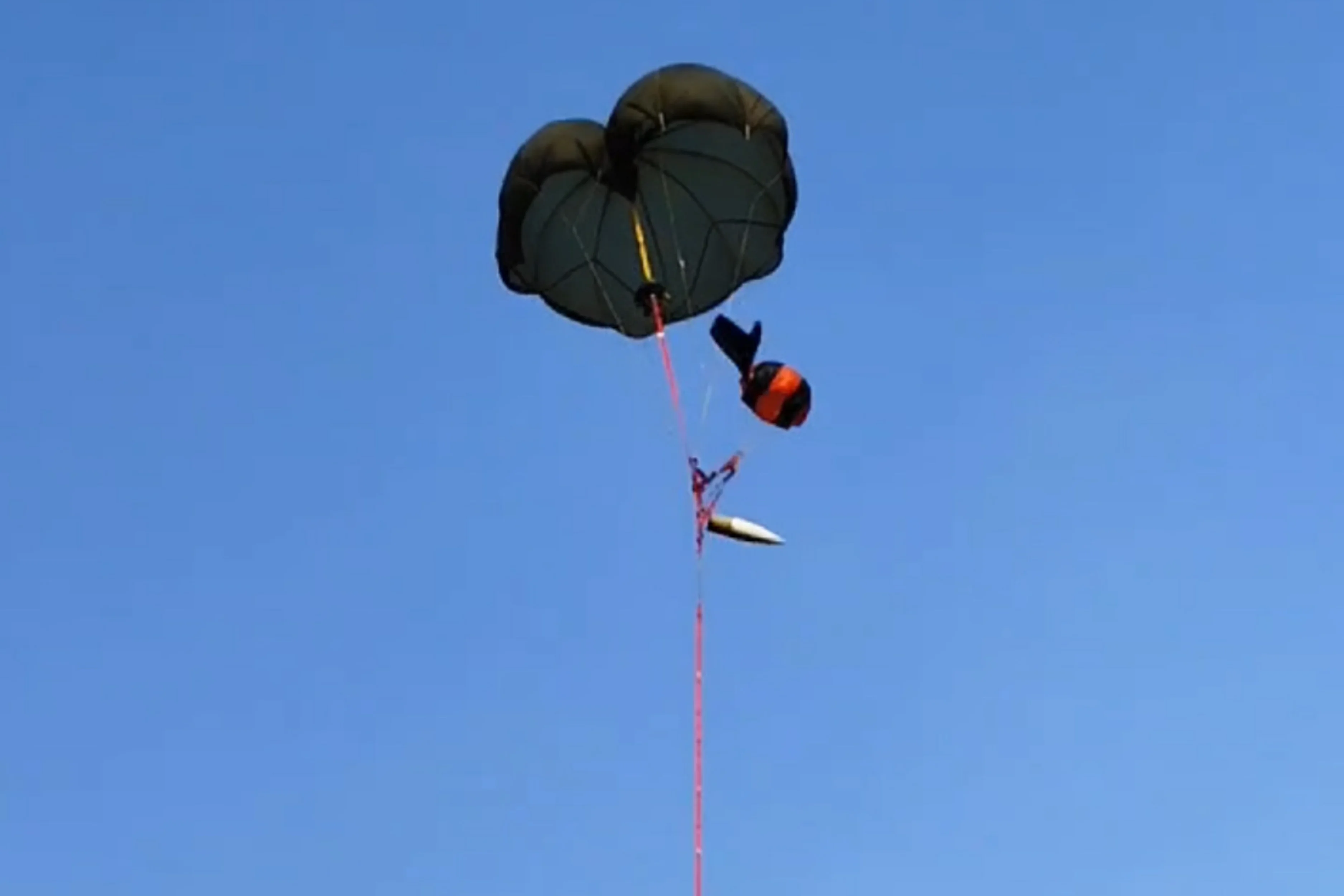
Launch, Recover and Relaunch